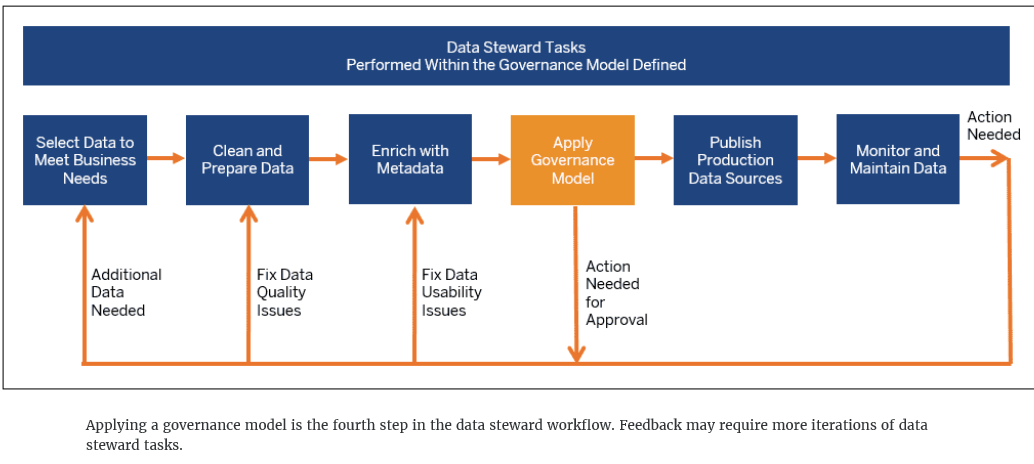
Applying a Governance Model
A published data source workflow is the cornerstone of a strong data governance strategy.
A data steward ushers the data source from a proposed metadata model to be ready for a production environment. The data workflow varies according to the governance model, which describes how the content is organized, as well as the functional groups/roles defined and their corresponding approval processes and permissions.
You have created a metadata model to provide a business context for the data. Next, you are ready to ensure that the governance model processes and controls are applied in order to get the data ready for publishing to production.
In order to get approval for publishing to a production environment, the data steward may have to iterate on tasks already completed.
Implementation of a governance model
How is a governance model implemented?
The governance model framework encompasses the people who understand and comply with the established controls, the data and content management processes, and the tools for implementation. Combining people, process, and technology creates a foundation for accountability and enables, rather than restricts, access to secure and trusted data for all skill levels in the organization. Note that some governance model framework pieces are repeatable processes that use company communication, such as approvals and announcements about data sources, and may not be implemented in Tableau.
When planning a site, the site administrator defines the audience, identifies the functional groups, and describes the workflow for the functional groups, including the interactions, decisions, and restrictions. The site admin implements the functional governance model, using licenses, site roles, projects, groups, and permissions on content and data, based on the controls, roles, and repeatable processes, to make the appropriate data and content available to the corresponding audience.
An overview of the implementation process:
- The site admin describes or creates a workflow for how data sources and workbooks will be created, managed, and published by the given functional groups.
- Data stewards/data admins use the established workflow to get data sources ready to be published in the production environment.
- Other users then work with certified production data sources and workbooks, according to the governance model workflow.
How do data workflows vary?
The workflow for data sources will vary according to the governance model definitions. Answers to the following questions will determine some of the key differences in workflows.
Example workflows
Direct access workflow
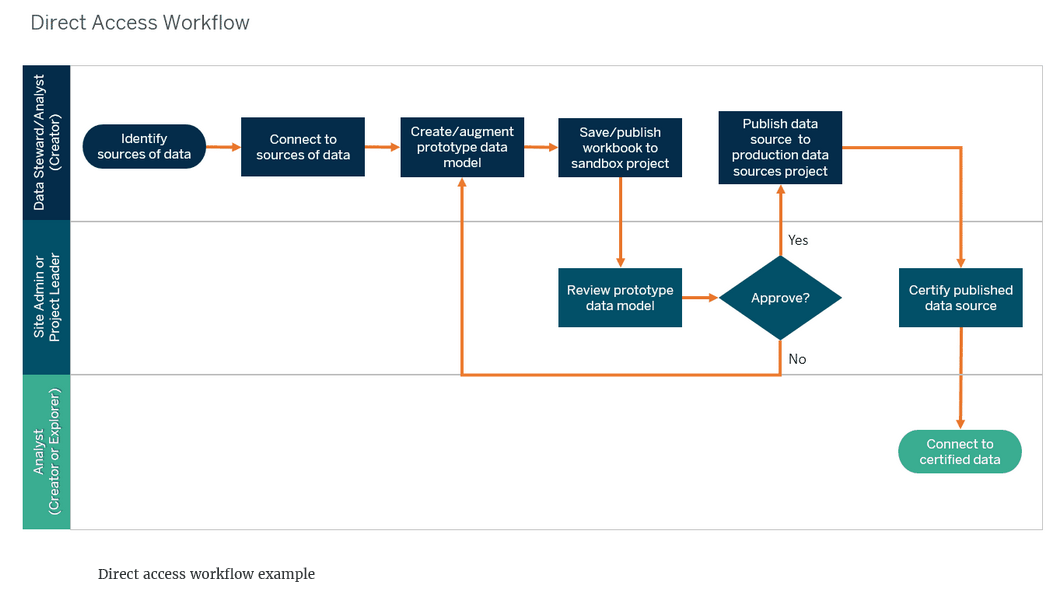
In this example from the Tableau Blueprint, Data Stewards and Analysts have direct access to sources of data. Data Stewards/Analysts prototype data sources as an embedded data source in a Tableau workbook in a sandbox project. Then, after review and approval of the prototype by others, the Data Stewards/Analysts create a published data source in a production project to share the curated data model, after it is certified.
Workflow process steps:
- Appropriate sources of data are identified to answer business questions.
- The Data Steward/Analyst:
- Connects to sources of data.
- Creates or augments a prototype/sandbox data model as an embedded data source in a Tableau workbook.
- Saves or publishes the workbook to a sandbox project on Tableau Server/Online.
- The Site Admin or Project Leader reviews the data model to ensure it complies with data standards and approves it.
- The Data Steward/Analyst publishes the data source to the production data source project.
- The Site Admin or Project Leader certifies the production data source.
- Users connect to the certified data source to create new content based on trusted data.
Restricted access workflow
In another workflow example described in the Tableau Blueprint, Analysts have restricted access to sources of data and rely on a Data Steward/DBA to provide the prototype data source embedded in a Tableau workbook. Then, after review, augmentation, and approval of the prototype by others, the Data Stewards/Analysts create a published data source in a production project to share the curated data model, after it is certified.
Restricted access workflow example
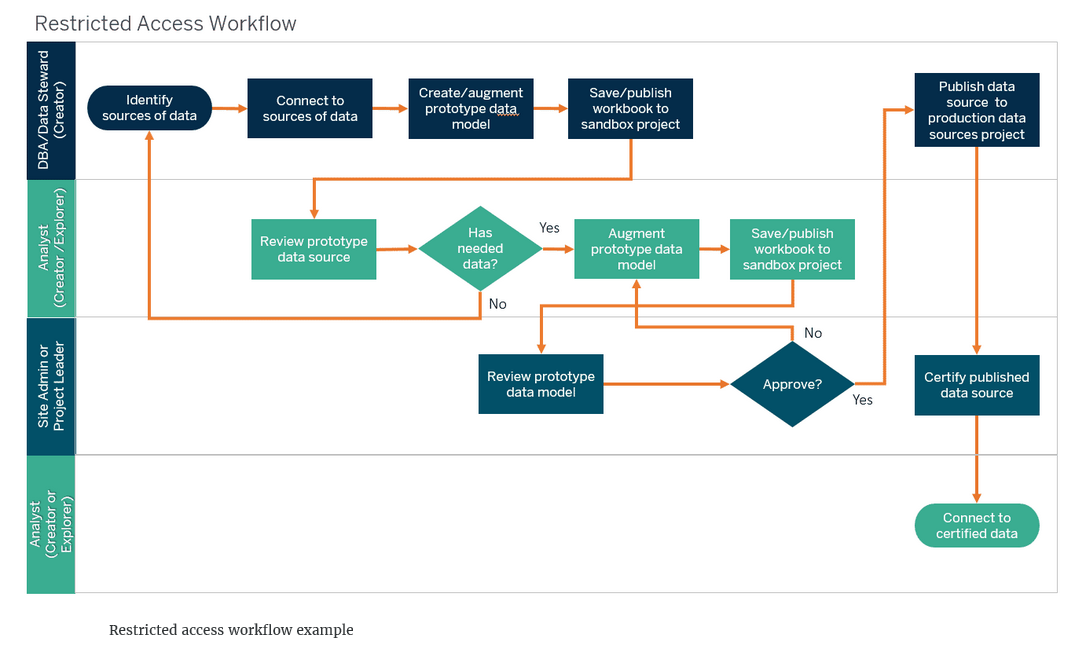
Workflow process steps:
- Appropriate sources of data are identified to answer business questions.
- The Data Steward/Database Administrator:
- Connects to sources of data.
- Creates or augments a prototype/sandbox data model as an embedded data source in a Tableau workbook.
- Saves or publishes the workbook to a sandbox project on Tableau Server.
- The Analyst reviews the prototype data source and augments the data model with new calculations, if necessary.
- The Site Administrator or Project Leader reviews the data model to ensure it complies with data standards and approves it.
- The Data Steward/DBA publishes the data source to the production data sources project.
- The Site Administrator or Project Leader certifies the production data source.
- Analysts connect to the certified data source to create new content based on trusted data.
In another example of a delegated governance model, workflows have been defined for several functional groups. In this example, Data Admins are fulfilling the Data Steward role.
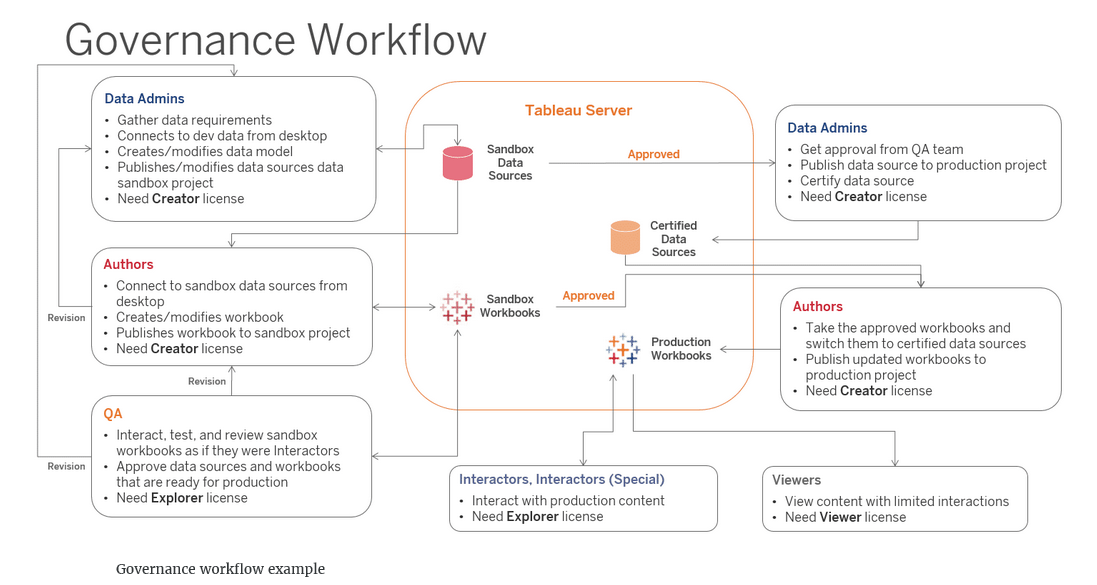
Project environment details
- The sandbox environment contains data sources and workbooks that are being developed. These sandbox data sources and workbooks will be tested, reviewed, and approved before being made available to the general sales team. Only data admins, authors, and the QA team need access to this environment.
- The production environment contains the production-level data sources and workbooks that have been tested and approved for use by the general sales organization. All members of the sales department, including data admins, authors, and the QA team, need access to this environment.
- The production environment also contains a location into which users can publish ad hoc content (not shown here). In this location, users only see the content that they published. They do not have access to the content of others. This allows the team to interact and save content for personal use.
Get approval to publish to production projects
When applying a governance model, expect to get valuable feedback before the data is ready to publish to the production environment. During this stage, the approver will usually check. If additional data is needed or would be beneficial to users, it is likely that the approver will request you to add in those fields.
The data will be validated against data quality standards for accuracy, completeness, and relevance. If issues are found, you will need to clean and prepare the data to address any problems. The metadata will be assessed to ensure data usability. It is common to get metadata requests, for example, to rename fields, hide fields, add definitions, and create calculated fields.